Gorham’s Disease
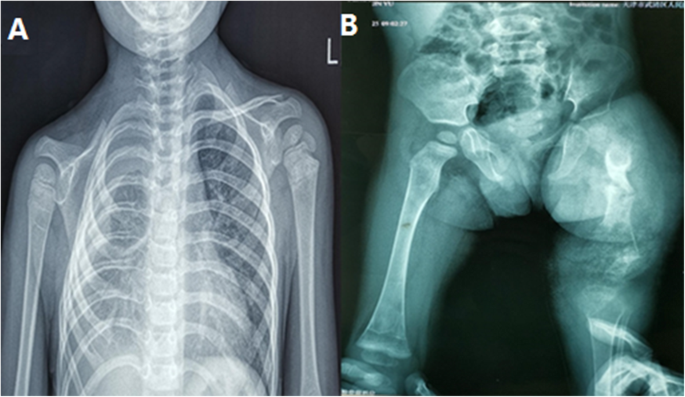
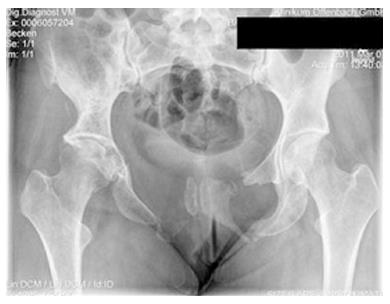
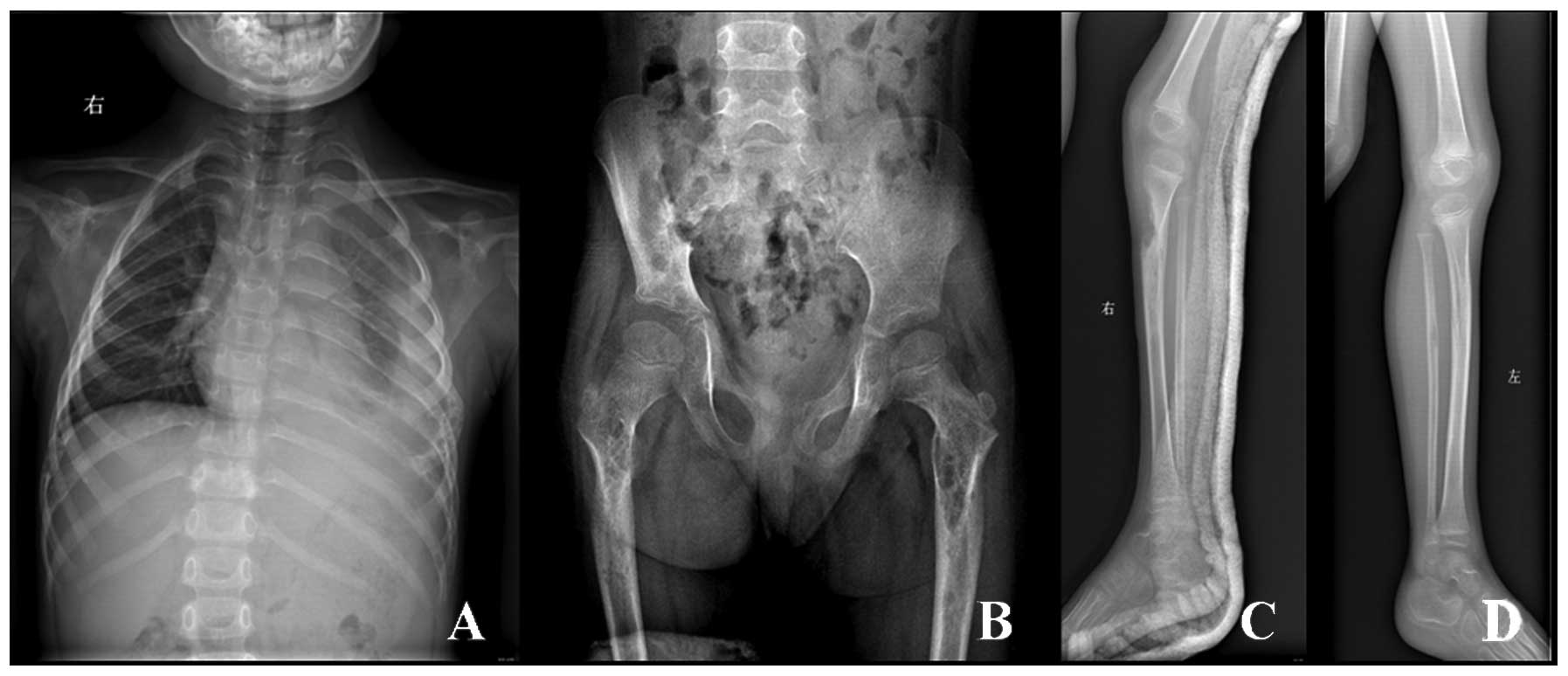
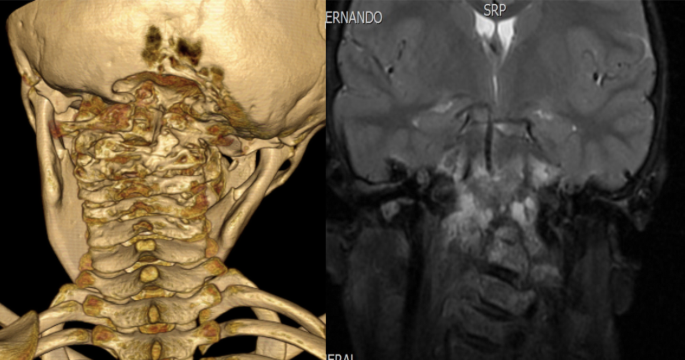
Gorham's disease. The ribs spine pelvis skull. Gorhams disease is a rare disorder characterized by osteolysis 14. Gorhams disease fortunately is an extremely rare disorder of the musculoskeletal system.
Gorhams disease GD is a rare form of lymphangiomatosis associated with profound osteolysis. Gorhams disease is a rare disorder characterized by proliferation of vascular channels that results in destruction and resorption of osseous matrix. Gorham-Stout may affect multiple bones but in most cases it is a regional disease meaning it stays in one region of the body.
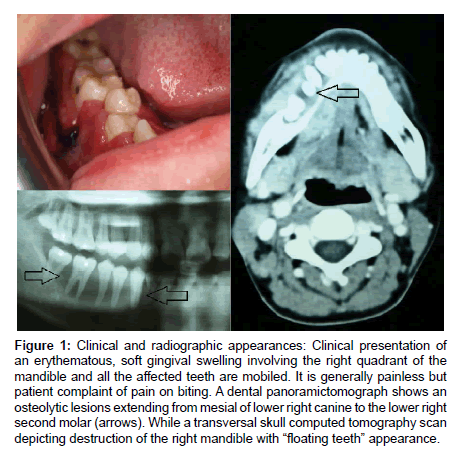
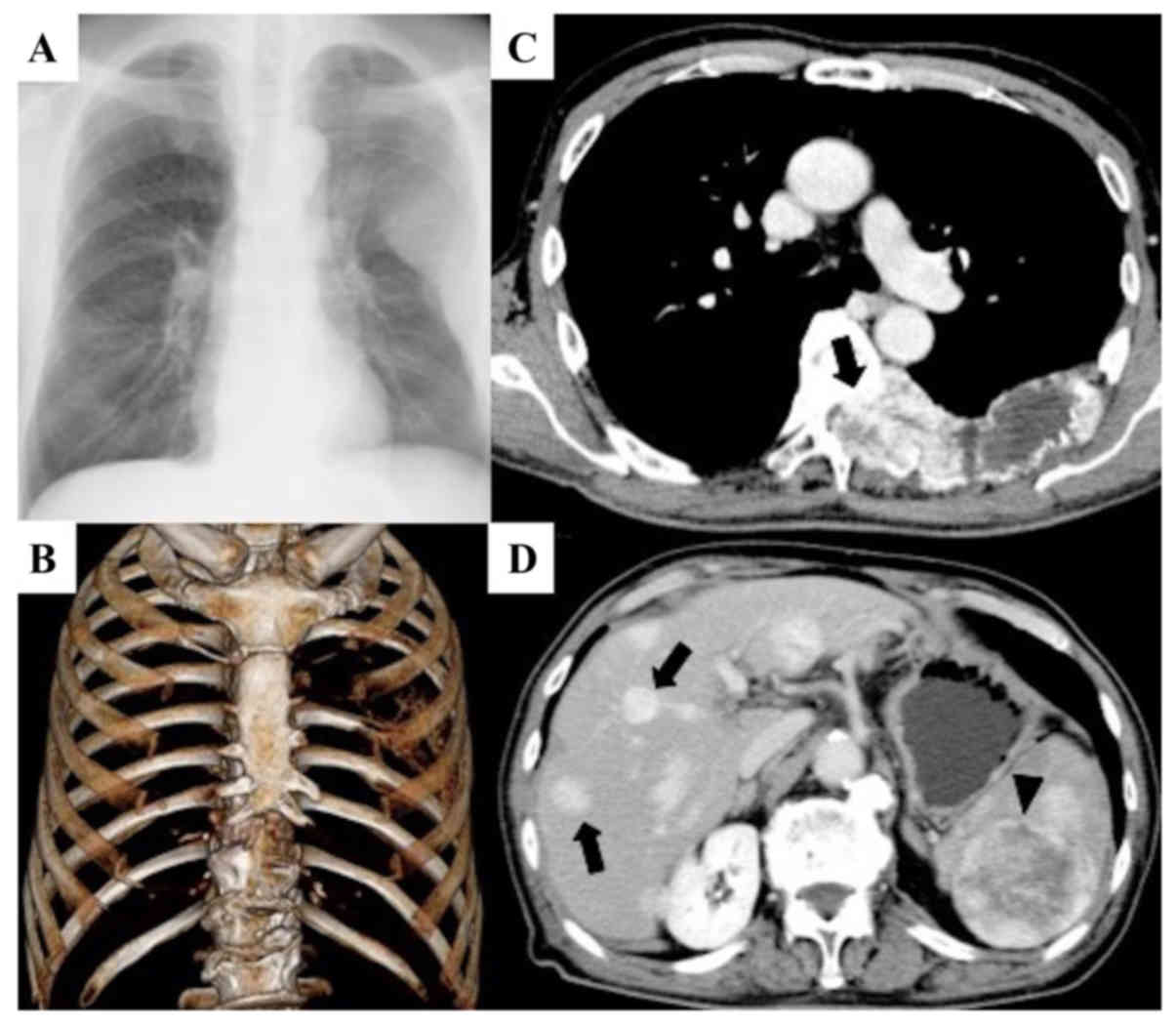
We report a case of an adolescent boy with massive osteolysis of the mandible in whom the diagnosis of Gorhams disease was. A chest radiograph showed osteolysis of the left first second and third ribs. Gorhams Disease also known by the name of Disappearing Bone Disease is an extremely uncommon medical condition of the skeletal system which does not have a specific etiology in which there is uncontrolled proliferation of lymphatic channels within the bone causing resorption and replacement of bone fibrosis.
The symptoms of GSD depend upon the specific bones involved. The exact cause of GSD. This patient eventually developed chylothorax and expired.
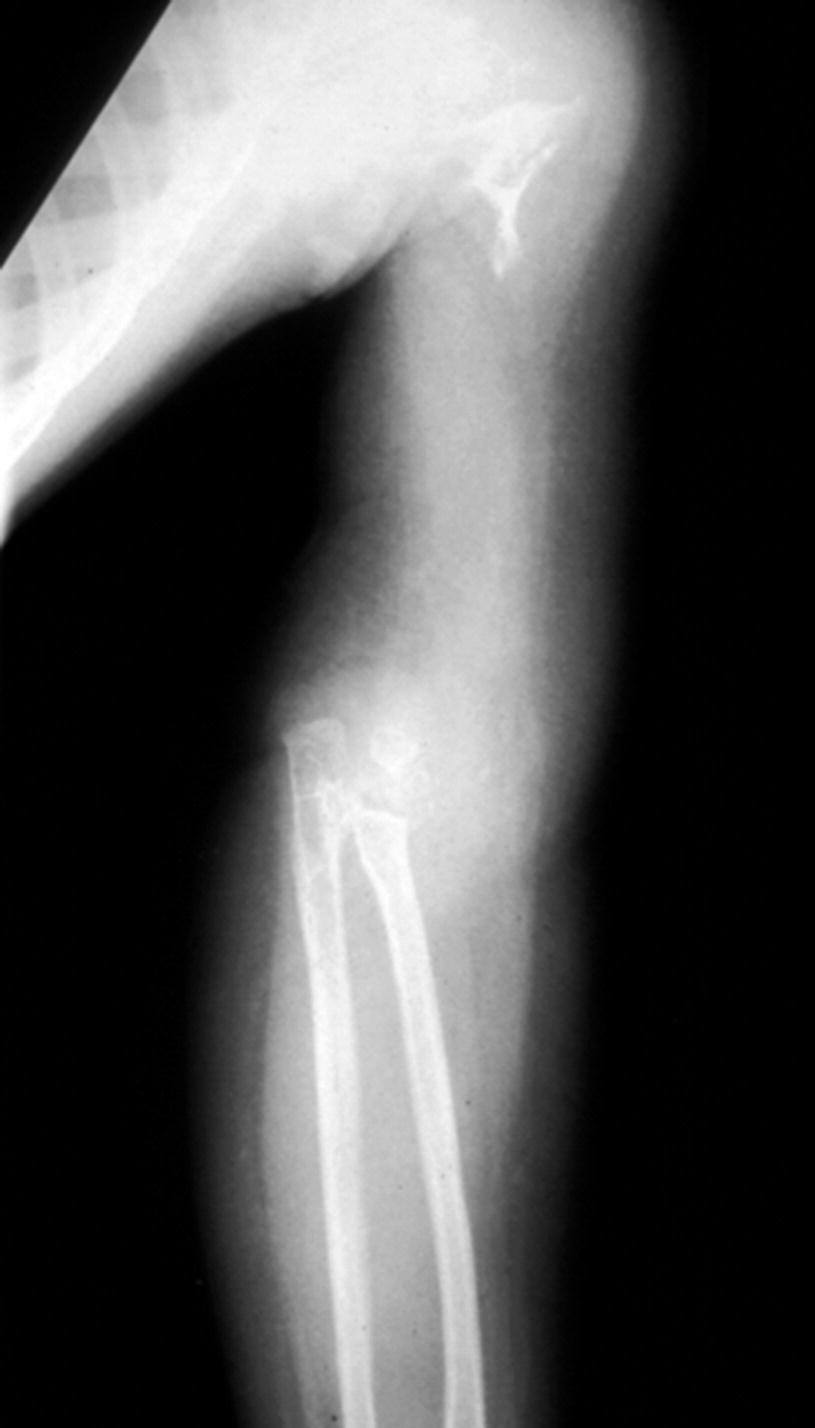
Small limb lesions can cause fractures while spinal involvement or chylothorax associated with rib lesions can be life threatening. In 1954 Gorham and colleagues1reported on two patients with massive osteolysis of the bone. Gorham-Stout Disease General Discussion.
Muchos ejemplos de oraciones traducidas contienen Gorhams disease Diccionario español-inglés y buscador de traducciones en español. Bone loss can occur in just one bone or spread to soft tissue and adjacent bones. AB - We report a case of Gorhams disease of the chest wall in a 29-year-old man.
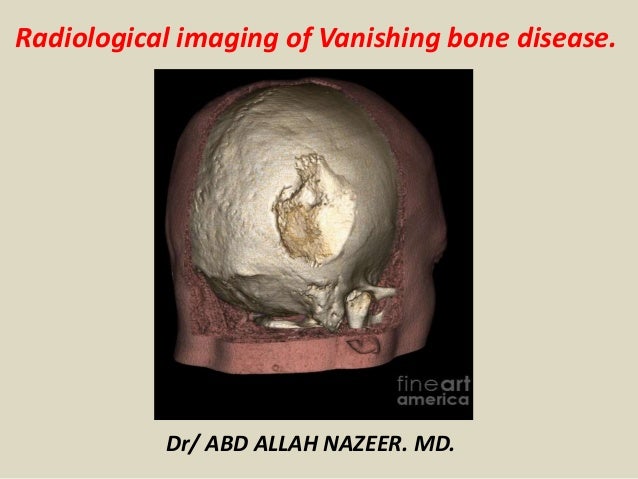
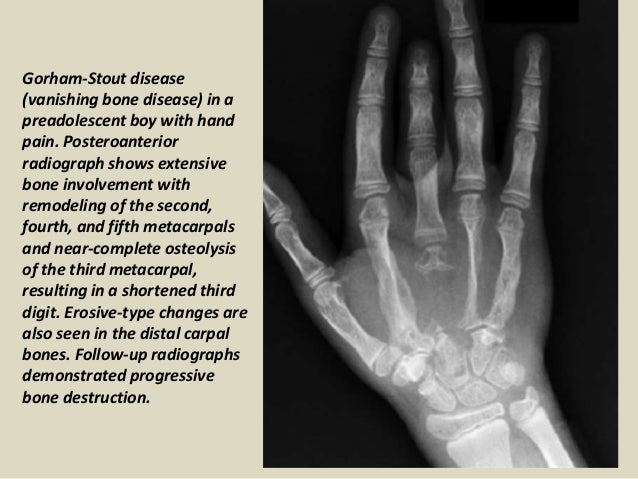
Gorham-Stout disease GSD which is also known as vanishing bone disease disappearing bone. It was first described by Jackson in 1838 but it was Gorham and Stout in 1955 who defined this disease as a specific.
Bone loss can occur in just one bone or spread to soft tissue and adjacent bones.
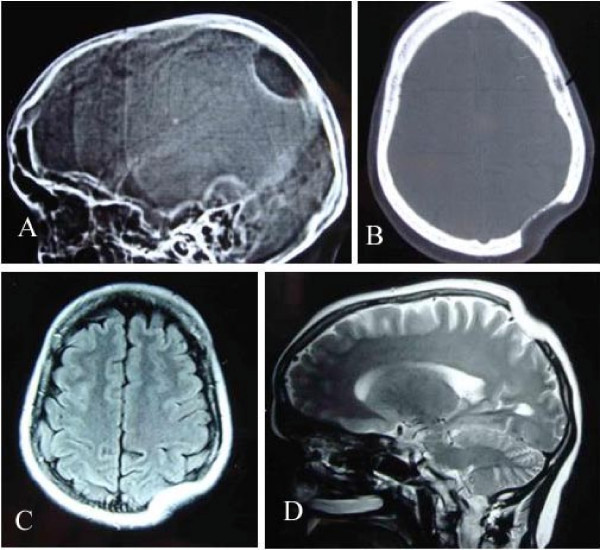
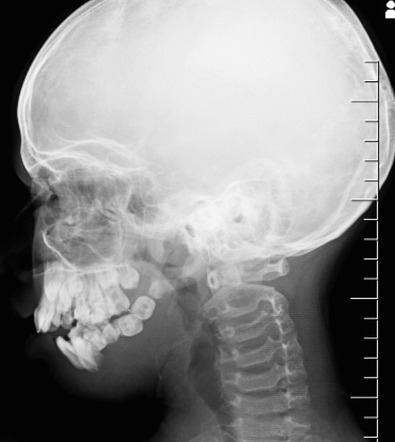
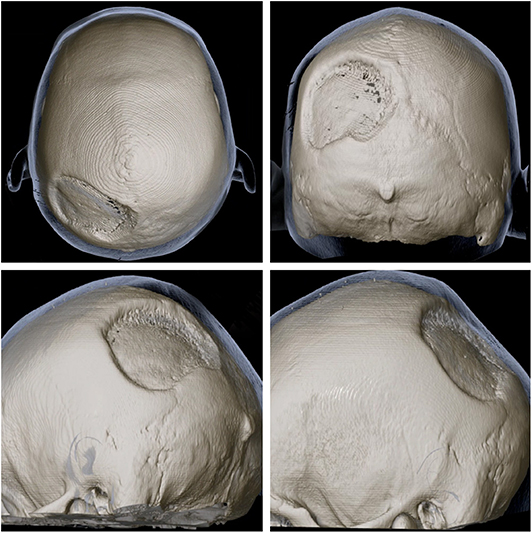
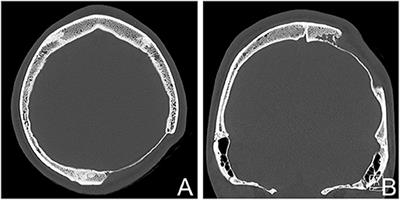
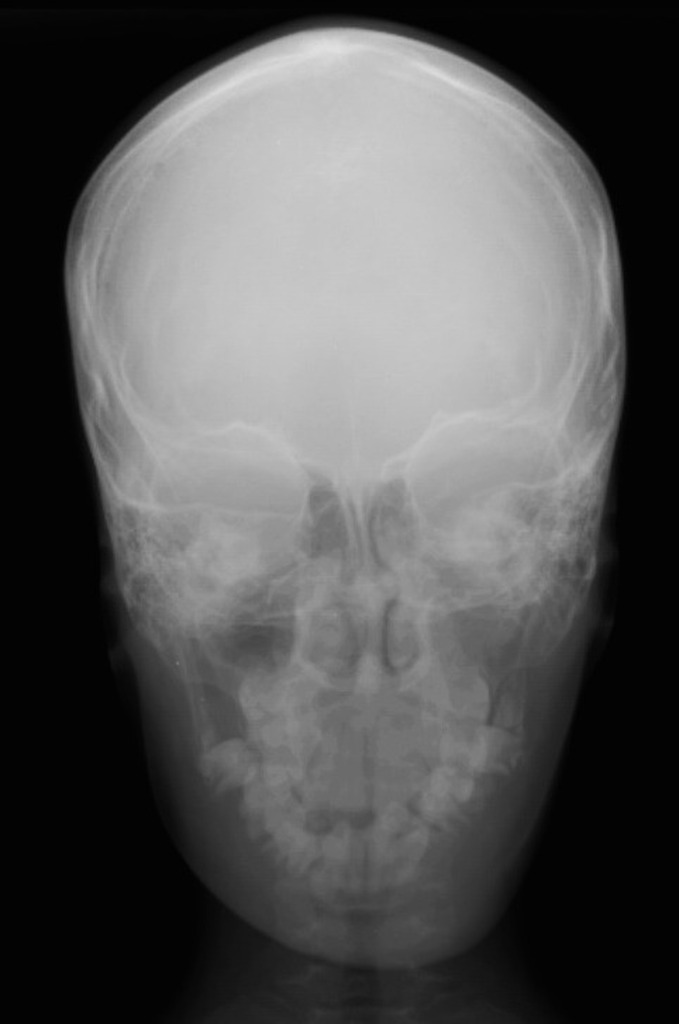
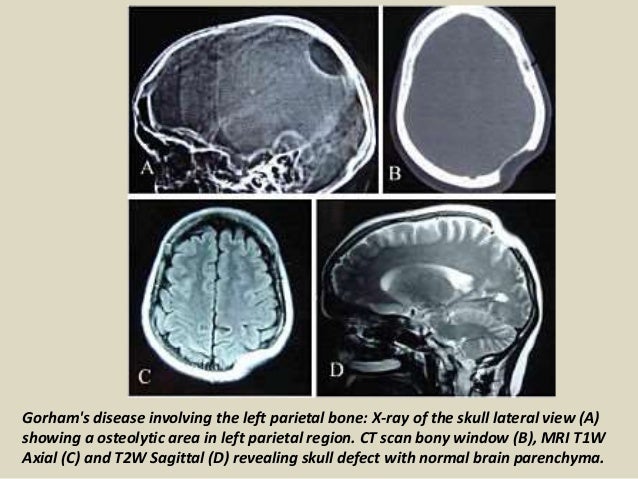
Bones commonly affected by Gorham-Stout include. Gorham-Stout Disease General Discussion. We report a case of an adolescent boy with massive osteolysis of the mandible in whom the diagnosis of Gorhams disease was. Outcome depends on the site affected. The symptoms of GSD depend upon the specific bones involved. Histopathologically normal bone is replaced by vascular lymphatic proliferation but not neoplastic proliferation 56. Gorham-Stout disease GSD which is also known as vanishing bone disease disappearing bone. The most conspicuous element of Gorhams disease is its radiographic features wherein massive disappearance of the mandible is observed. In 1954 Gorham and colleagues1reported on two patients with massive osteolysis of the bone.
AB - We report a case of Gorhams disease of the chest wall in a 29-year-old man. This patient eventually developed chylothorax and expired. Gorhams disease GD is a rare form of lymphangiomatosis associated with profound osteolysis. Gorhams Disease also known by the name of Disappearing Bone Disease is an extremely uncommon medical condition of the skeletal system which does not have a specific etiology in which there is uncontrolled proliferation of lymphatic channels within the bone causing resorption and replacement of bone fibrosis. Bones commonly affected by Gorham-Stout include. The most conspicuous element of Gorhams disease is its radiographic features wherein massive disappearance of the mandible is observed. Of the two cases one was a boy 16 years of age with right clavicle and scapula involvement.





























Post a Comment for "Gorham’s Disease"